VEGETABLE OILS Prior loading of any Veg Oil cargoes, it should be noted that the last three cargoes must be lead-free.Also, ensure all Cargo Tanks, pipelines and pumps must be well drained and dried.The Veg Oils are very susceptible to Salt Water. Any contact with Sea water will result in rotting /damage of cargo.It should be ensured that after loading is completed; all cargo tanks are checked by Ship’s Officer along with attending surveyor, with a bottom sampler to ensure no water is trapped/loaded at Load Port.All Butterworth openings should have Oil resistant packing’s. … [Read more...]
Archives for November 2015
What is VEF (Vessel Experience Factor) ?
The VEF is a factor to account for residual inherent measurement imprecision associated with ships's calibration and residual random measurement variations (both ship and shore). The VEF is a computation of the history of the Total Calculated Volume (TCV) loaded by the vessel adjusted for OBQ or ROB, compared with the TCV of shore measurements, typically a Bill of Lading in order to compute a load port VEF for the vessel.The VEF should always be used by the vessel to assess if the Bill of Lading quantity is reliable. It may also provide an indication of potential shortages on outturn at … [Read more...]
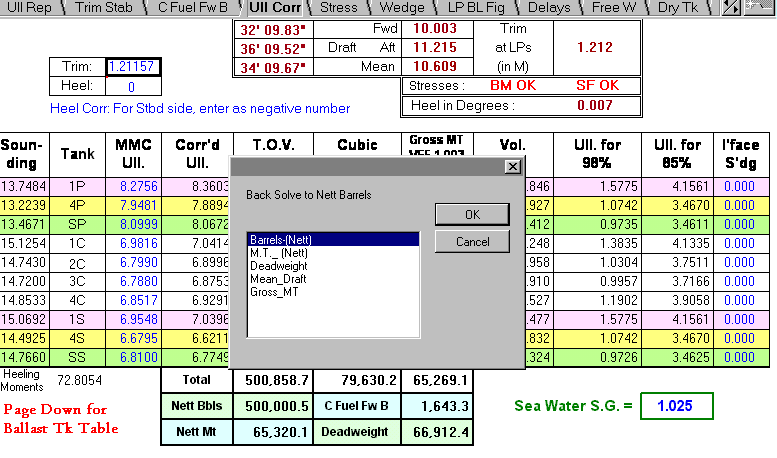
Cargo Calculations – Tanker Work
General An oil volume can only be measured at its prevailing temperature and it, therefore, follows that the standard volume must usually be calculated. Unfortunately, different countries have different standard (reference) temperatures.Generally, the reference temperatures are:In Eastern Bloc, Brazil 20oC; In Western Europe 15oC; In the USA 60oF. The situation is further confused in that there are primarily two volumetric units, which are:In metric countries the cubic meter (m ) In non-metric countries the barrel (Bbl).Combining a statement of volume … [Read more...]
Deck Water Seal – Inert Gas System on Tankers
Deck Water Seal In an inert gas system onboard Tanker ships, Deck water seal is the principal barrier. A water seal is fitted which permits inert gas to be delivered to the deck main but prevents any backflow of cargo gas even when the inert gas plant is shut down. It is vital that a supply of water is maintained to the seal at all times, particularly when the inert gas plant is shut down. In addition, drains should be led directly overboard and should not pass through the machinery spaces.There are different designs but one of three principal types may be adopted: Wet type This is … [Read more...]
OIL TANKER OPERATIONS (Discharging) – Conventional Tanker Basics
OIL TANKER OPERATIONS (Discharging) Good planning is the hallmark of efficient tanker operations.Prior arriving at the discharge port an exchange of information between the ship and the terminal will take place. Once the vessel is tied up at the terminal, a ship-shore checklist will have to be filled out. The general safety checks and precautions will be the same as given for the loadport. Since pumps will be running at the discharge port, special attention will have to be given to monitor the safe running of the pumps. Pumproom ventilation should be running throughout operations. Proper … [Read more...]
OIL TANKER OPERATIONS (Loading) – Conventional Tanker Basics
Good planning is the hallmark of efficient tanker operations. Before a tanker approaches port, there are several factors that must be considered:Testing of cargo/ballast valves, sea valves, pipelines, pumps, inert gas systems, emergency stops. Preparedness of fire-fighting, life-saving and anti-pollution equipment. A pollution drill held before a ship arrives in port will serve the purpose of checking ail equipment. Any response during an emergency will be good since a drill had been executed recently. Preparation of tanks, including readiness of slop tanks. Planning for proper … [Read more...]
Pump Types / Characteristics – Tanker Basics
There are many types of pumps, each with its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. Basically, pumps can be broadly categorised into 3 types :Non-positive-displacement pumps e.g. centrifugal pumps Positive displacement pumps e.g. reciprocating pumps, gear pumps, screw pumps, etc. Special devices like eductors which can also be included in this category.Centrifugal Pumps This type of pump does not have a self-priming capability. Consequently, it operates best only when there is a positive head on the suction side. However, this pump has the distinct capability of … [Read more...]
Piping Arrangement – Conventional Oil Tanker Basics
The arrangement of loading and discharge lines is collectively known as the Ship’s Cargo System. The first oil tankers to carry petroleum products in bulk were equipped with very simple pumping systems. For the most part, they had a single line which ran forward and aft from a midship pump-room, in which were housed two steam reciprocating pumps. One pump served the tanks forward of the pump-room, while the other dealt with the oil from the tanks aft of this pump-room. Some of the more simple types with their engines amidships provided pumps in the engine room to handle the cargo, or … [Read more...]
FLAMMABILITY COMPOSITION DIAGRAM
Flammability DiagramThe diagram given above (Flammability Composition Diagram) can be considered the most important diagram to understand the concept of flammability.Hydrocarbon gas normally encountered in petroleum tankers cannot burn in an atmosphere containing less than approximately 11% oxygen by volume. Accordingly, one way to provide protection against fire or explosion in the vapour space of cargo tanks is to keep the oxygen level below that figure.The flammable limits vary for different pure hydrocarbon gases and for mixtures derived from different liquids. For practical … [Read more...]
Tanker Terminology used in Shipping
Tanker Terminology Anti-static additiveA substance added to a petroleum product to raise its electrical conductivity to a safe level above 50 picoSiemens/metre (pS/m) to prevent accumulation of static electricity. Auto-ignitionThe ignition of a combustible material without initiation by a spark or flame, when the material has been raised to a temperature at which self-sustaining combustion occurs. BondingThe connecting together of metal parts to ensure electrical continuity. Brush dischargeA brush discharge is a diffuse discharge from a single blunt … [Read more...]